Installing a Master Clock System on an FPSO Vessel
Installing a master clock system on an FPSO vessel is a critical task that enhances synchronization, efficiency, and safety.
Given the complexity and scale of operations on an FPSO, maintaining precise and synchronized timing across all systems is crucial. A master clock system ensures that all systems onboard operate in harmony, preventing costly errors and enhancing operational efficiency.

Why a Master Clock System?
Synchronization: Ensures all onboard systems and equipment operate on the same time, which is essential for data logging, communications, and coordination.
Efficiency: Improves operational efficiency by reducing discrepancies in timing.
Safety: Enhances safety by ensuring time-critical operations are synchronized.
Components of a Master Clock System
A master clock system is a comprehensive setup designed to provide precise and synchronized timekeeping across various systems and devices. On an FPSO vessel, this synchronization is crucial for operations, safety, and communication. Here are the key components of a master clock system:
Master Clock
Central Unit: The master clock serves as the primary time source for the entire system. It receives time signals from a highly accurate reference, such as GPS or an atomic clock.
Time Source: The master clock often uses GPS signals to maintain accurate time. Some systems may also use other time sources like Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers or radio signals.
Interfaces: Includes various communication interfaces (e.g., Ethernet, RS-232, RS-485) to connect with slave clocks and other systems.
Slave Clocks
Digital Displays: These clocks receive time signals from the master clock and display the synchronized time. They can be installed throughout the vessel for visibility in different locations.
Analog Displays: Some systems might use traditional analog clocks, which are also synchronized with the master clock.
Wireless or Wired: Slave clocks can be connected to the master clock either through wired connections or wirelessly, depending on the system design.
Signal Distribution Network
Cabling: High-quality cables are used to transmit time signals from the master clock to the slave clocks. Ethernet cables are commonly used for networked systems.
Switches and Routers: Network switches and routers manage the data flow and ensure that time signals are distributed correctly to all connected devices.
Wireless Transmitters and Receivers: In wireless systems, transmitters and receivers facilitate the distribution of time signals without the need for extensive cabling.
Synchronization Modules
NTP Servers: Network Time Protocol servers ensure that all networked devices receive accurate time signals. They can act as intermediaries between the master clock and other systems.
Time Code Generators: These devices generate various time codes (e.g., IRIG-B, SMPTE) that can be used by different types of equipment requiring synchronized time.
Power Supply Units
Main Power Supply: Provides the necessary power to the master clock and associated components. It must be stable and reliable to ensure continuous operation.
Backup Power Supply: Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) or battery backups ensure that the master clock system remains operational during power outages.
Antenna System
GPS Antenna: Captures GPS signals for the master clock. It is usually installed in a location with a clear view of the sky to ensure reliable signal reception.
Cable and Connectors: High-quality coaxial cables and connectors are used to connect the GPS antenna to the master clock, minimizing signal loss.
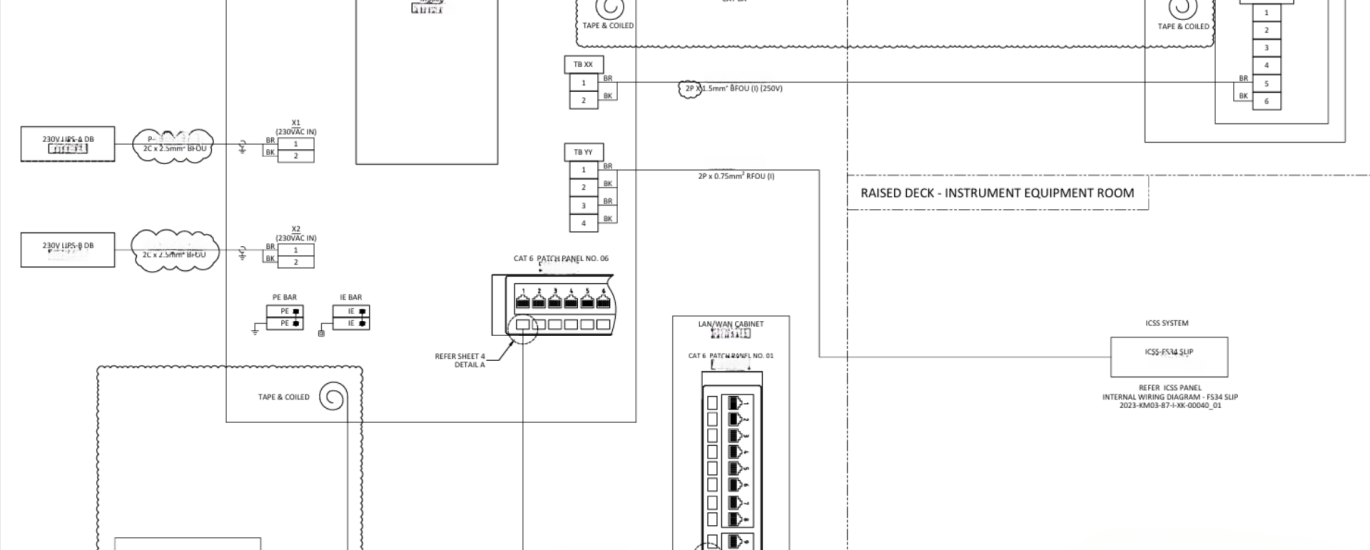
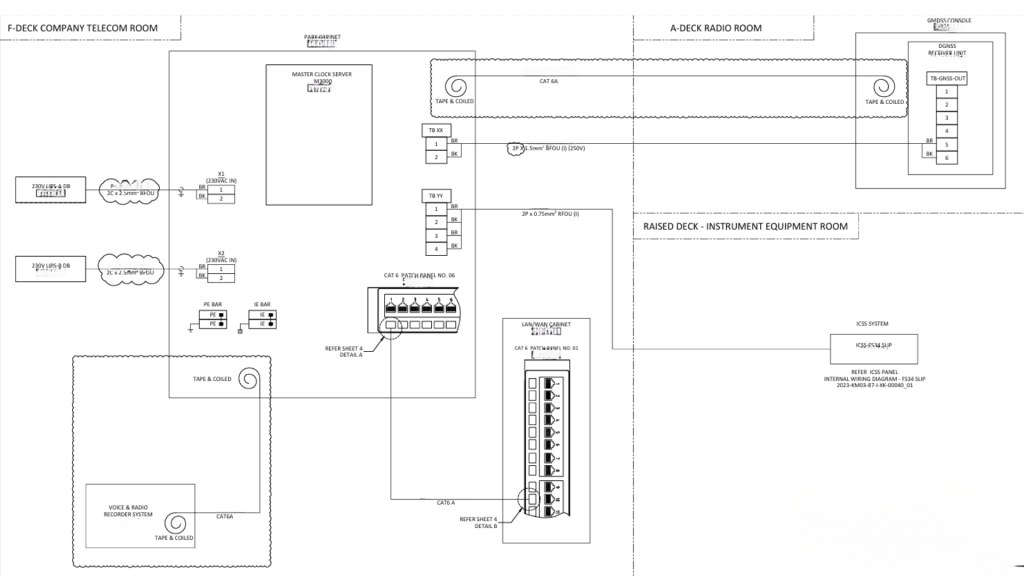
Master Clock Installation Summary
System Design: Design the network layout, including the master clock, slave clocks, and necessary cabling while ensure redundancy to prevent system failure.
Power Supply: Ensure a stable and uninterrupted power supply for the master clock system.
Installation of Master Clock: Install the master clock in a secure and accessible location, typically in the control room or equipment room. Connect the master clock to the vessel’s power supply and network. Use appropriate connectors and cabling as per the manufacturer’s specifications. Configure the master clock with the correct time settings. This may involve synchronizing with a GPS signal or another accurate time source.
Installation of Slave Clocks: Install slave clocks at designated locations across the FPSO, ensuring they are visible to relevant personnel. Ensure proper cabling and connectors are used to maintain signal integrity.
Integration Testing: Test the integration of the master clock system with other onboard systems, such as navigation and communication systems.
get the Right Team
Proper installation, configuration, and maintenance of these components are essential for the system’s success and the overall efficiency and safety of the vessel’s operations. Team Vivo Asia is experienced in the installation and configuration of systems for FPSO vessels. We are well-versed in industry regulations and compliance requirements!