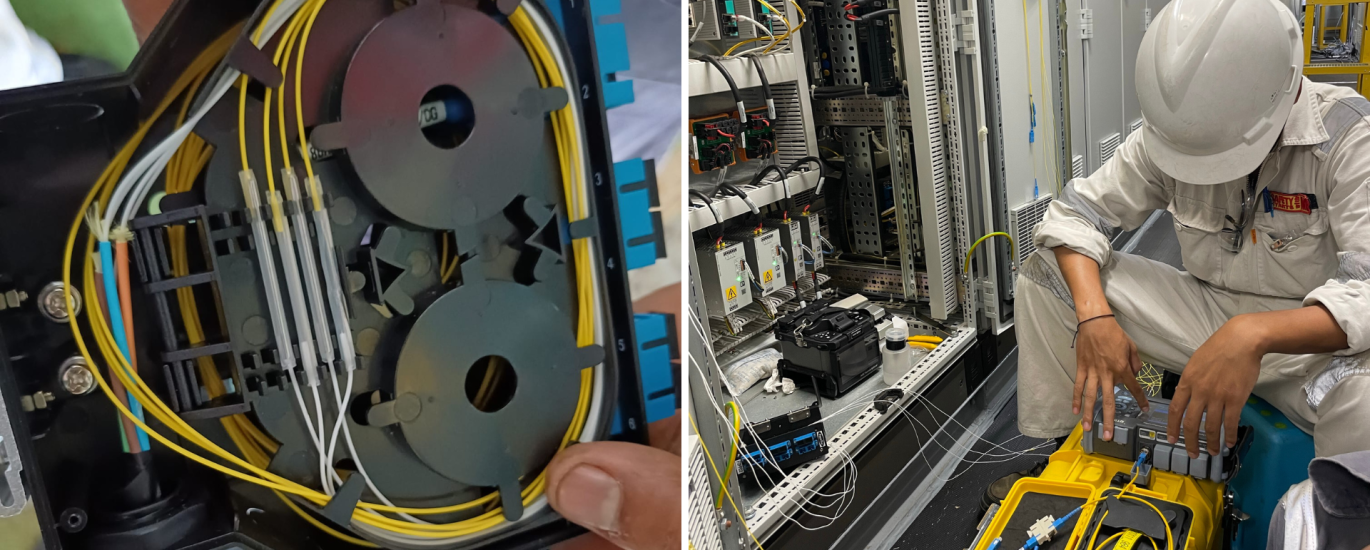
As maritime vessels continue to embrace the digital age, the integration of robust fiber optic termination and testing practices becomes imperative.
Navigating the challenges of the open sea requires a reliable and resilient communication infrastructure. Through proper termination techniques and rigorous testing procedures, maritime professionals can ensure that their vessels stay connected, no matter how vast the ocean may be.
Fiber optic termination involves the process of connecting optical fibers to various components, such as connectors, splices, and network devices. This ensures a secure and efficient data transmission pathway. Fiber optics have revolutionized communication at sea, providing high-speed internet, robust data transfer for navigation systems, and reliable communication between different parts of the vessel.
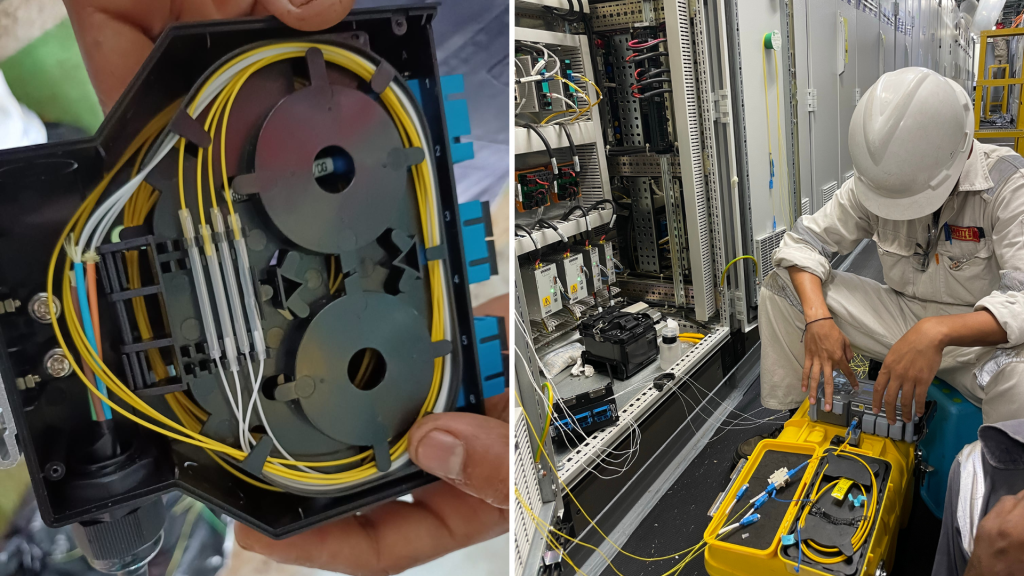

Fiber Optic Termination on Maritime Vessels
Challenges Unique to Maritime Environments
Harsh environmental conditions, such as saltwater exposure, temperature variations, and constant vibrations, pose challenges for maintaining fiber optic connections. Termination solutions must be resilient to these elements.
Waterproofing and Corrosion Resistance
Specialized connectors and termination equipment are essential to protect against water ingress and corrosion. Some examples include:
- Sealed Connectors: Utilizing connectors specifically designed for maritime environments with tight seals and O-rings can prevent water ingress
- Potted Connectors: This involves encapsulating the connection points with a potting compound or resin. This not only provides mechanical protection but also creates a waterproof barrier, shielding the connection from moisture and environmental contaminants.
- Heat Shrink Tubing: Applying heat shrink tubing with adhesive lining creates a watertight seal around connectors and splices. The adhesive lining forms a secure bond, preventing water from penetrating the connection points.
- Waterproof Enclosures: Housing fiber optic terminations within waterproof enclosures or bulkheads adds an additional layer of protection. These enclosures are designed to resist water penetration and can be equipped with seals and gaskets to ensure a secure environment for the fiber optic components.
- Cable Gland Seal: Cable glands with sealing mechanisms are used to pass fiber optic cables through bulkheads and enclosures while maintaining a waterproof seal. These seals are designed to prevent water from entering the vessel through cable entry points.
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials: Using materials that are resistant to corrosion, such as stainless steel or specialized alloys, for connectors and termination points is essential in maritime environments.
Fiber Optic Cable Routing and Management
Effective fiber optic cable routing and management are crucial on maritime vessels, where space is limited, and cables are exposed to constant movement, vibrations, and environmental challenges.
- Route Planning: Plan the routes of fiber optic cables to follow optimal pathways, avoiding areas prone to physical damage or interference. Consideration should be given to avoiding areas with high electromagnetic interference. Keep fiber optic cables separated from power cables to prevent electromagnetic interference. Crossing paths with high-voltage cables can induce unwanted signals in the fiber optics.
- Strain Relief and Slack Management: Implement strain relief systems at connection points and junctions to absorb any tension or stress on the cables caused by vessel movement. This helps prevent damage to connectors and ensures stable connections. Allow for the proper storage of cable slack to accommodate vessel movement and vibrations. Excess tension on cables can lead to performance issues and premature wear.
- Marking and Labeling: Mark and label fiber optic cables at regular intervals for easy identification during maintenance or troubleshooting. This is especially important in complex systems with numerous cables. Maintain comprehensive documentation of the cable routing layout, including information on cable types, connectors, and termination points.

Fiber Optic Testing at Sea
Rigorous testing is essential to guarantee the reliability of fiber optic connections on maritime vessels. Three essential testing methods are insertion loss testing, reflectometry, and optical time-domain reflectometry (OTDR).
- Insertion Loss Testing: Also known as attenuation testing, measures the amount of signal loss that occurs as light passes through a fiber optic component, such as connectors, splices, and couplers.
- Reflectometry: A testing method used to locate faults, such as breaks, bends, or splices, in a fiber optic cable by measuring the reflections of light.
- OTDR: An advanced testing method that provides detailed insights into the characteristics of a fiber optic cable, including the location and magnitude of losses, splice points, and breaks.
get the right team
It is clear that proper termination techniques and rigorous testing procedures, are required to ensure that vessels stay connected, no matter how vast the ocean may be. Getting the right team on the job is crucial, as skill and industry experience is essential when carrying our fiber optic termination and testing on board maritime vessels.
Vivo Asia is an expert fiber optic termination and testing, especially on board FPSO vessels. Our highly trained technicians are well versed in industry compliances, are familiar with the systems used and have proper testing equipment. Enquire today!