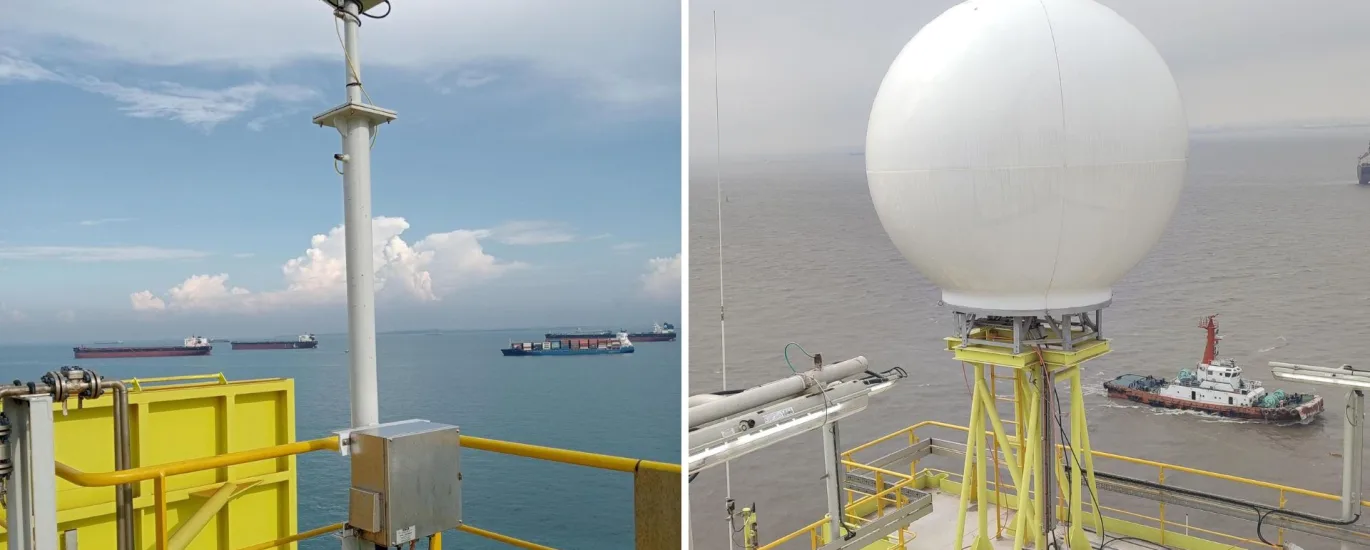
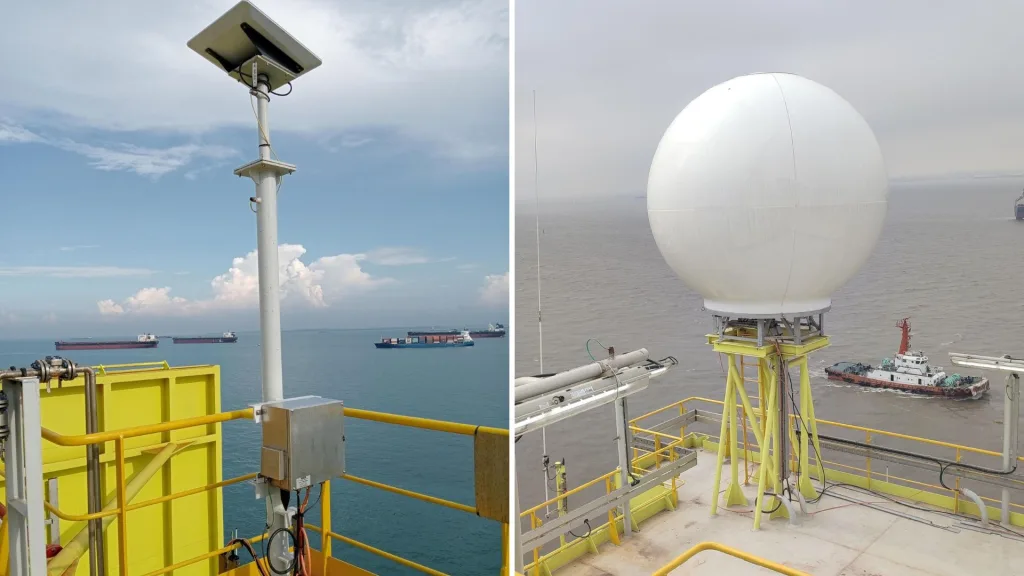
Optimizing antenna positioning on maritime vessels is critical for ensuring reliable communication and navigation. In the world of maritime communication, effective antenna placement ensures robust and reliable connectivity, crucial for navigation, communication, and safety. This blog delves into the key considerations and best practices for positioning antennas on maritime vessels.
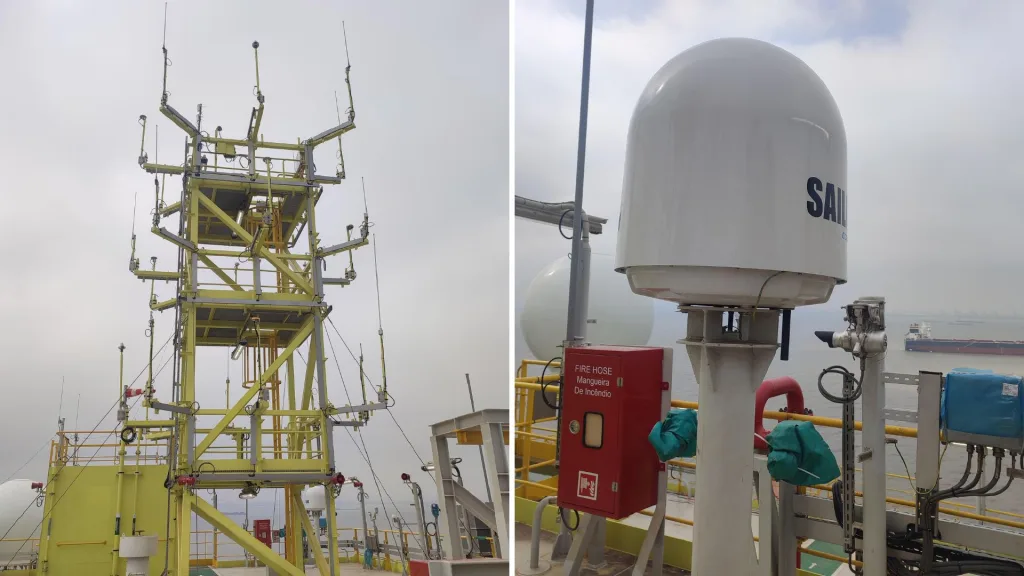

Understanding the Types of Maritime Antennas
Before diving into positioning strategies, it’s essential to recognize the common types of antennas used on maritime vessels:
VHF (Very High Frequency) Antennas: Primarily used for ship-to-ship and ship-to-shore communication.
HF (High Frequency) Antennas: Used for long-distance communication.
GPS Antennas: Crucial for navigation and positioning.
Satellite Antennas: Provide broadband communication for internet and voice services.
Radar Antennas: Used for detecting other vessels, landmasses, and weather patterns.
Key Considerations for Antenna Placement
Each of these antennas has unique requirements and challenges when it comes to positioning.
Height and Line of Sight
Height Advantage: Higher placement generally improves the line of sight, critical for VHF and radar antennas. Elevated antennas reduce obstructions caused by the vessel’s structure and enhance signal range.
Top Mast: For optimal performance, VHF antennas are typically mounted on the top mast. This location ensures maximum range and minimizes the chances of obstruction.
Separation and Interference
Minimize Interference: Different antennas should be placed sufficiently apart to avoid electromagnetic interference. For example, VHF and HF antennas should not be installed close to each other.
Horizontal Separation: A good rule of thumb is to maintain at least a few meters of horizontal separation between antennas to prevent cross-interference and signal degradation.
Structural Considerations
Metallic Structures: Metal can reflect and block signals, leading to dead zones. Avoid placing antennas near large metallic structures like cranes or masts.
Mounting Hardware: Ensure the mounting hardware is robust and resistant to corrosion, as maritime environments are harsh and saltwater can accelerate wear and tear.

Maintenance and Accessibility
Ease of Access: Antennas need regular maintenance and inspection. Position them in places that are accessible without endangering the crew.
Protected Locations: While height is important, ensure antennas are also protected from potential physical damage due to rough seas or during cargo handling operations.
Cable Management
Shortest Path: Run cables via the shortest possible path to reduce signal loss. Use high-quality, marine-grade coaxial cables to maintain signal integrity.
Protection: Protect cables from physical damage and environmental exposure using conduits and grommets.
get the right Team
By considering height, separation, structural impacts, maintenance, and cable management, you can enhance the performance and longevity of your maritime antennas. Engage with marine communication experts like Team Vivo Asia to keep your vessel connected, safe, and operationally efficient. We are well versed in guidelines from regulatory bodies like the International Maritime Organization (IMO).